Comprehensive Guide to Heavy-Gauge Thermoforming
What is Heavy-Gauge Thermoforming?
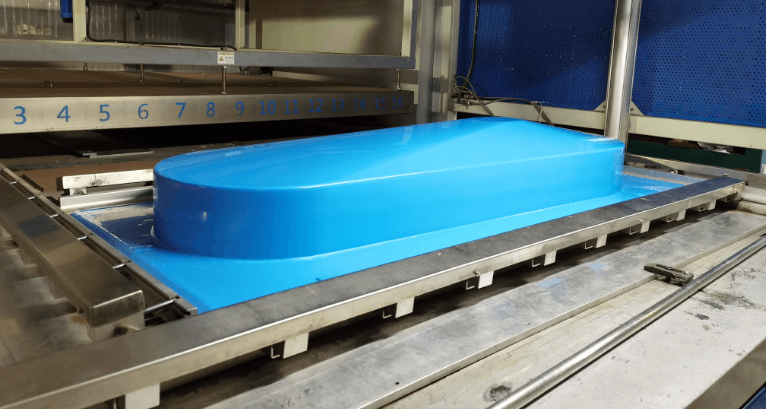
Heavy-gauge thermoforming is a manufacturing process where plastic sheets greater than 3.0 mm thick are heated and molded into durable, long-lasting parts. Unlike thin-gauge thermoforming, which focuses on disposable products like food containers, heavy-gauge thermoforming creates permanent, industrial components such as automotive panels, medical equipment housings, and aircraft interiors.
Heavy-Gauge vs. Thin-Gauge Thermoforming
The main differences between heavy-gauge and thin-gauge thermoforming include:
- Material Thickness: Heavy-gauge uses sheets thicker than 3.0 mm, while thin-gauge is typically less than 1.5 mm.
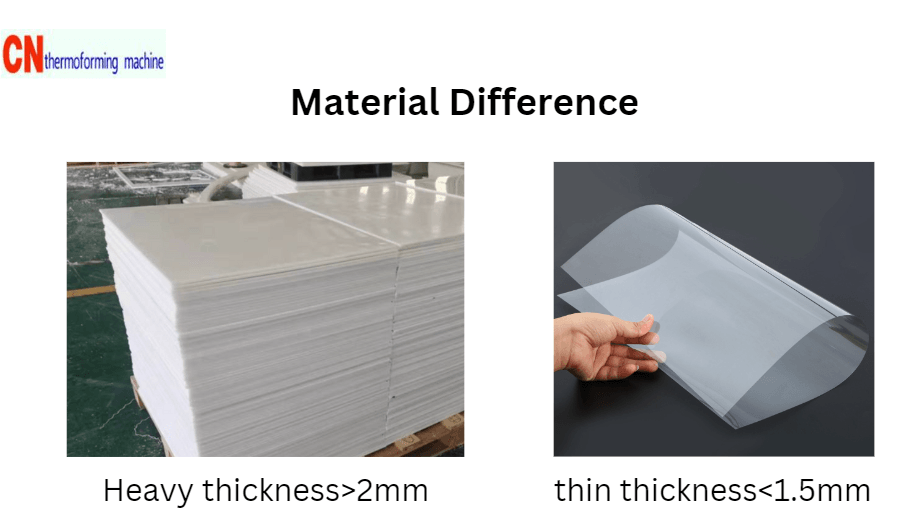
- Applications: Thin-gauge products are often disposable, whereas heavy-gauge products are for industrial or durable applications.

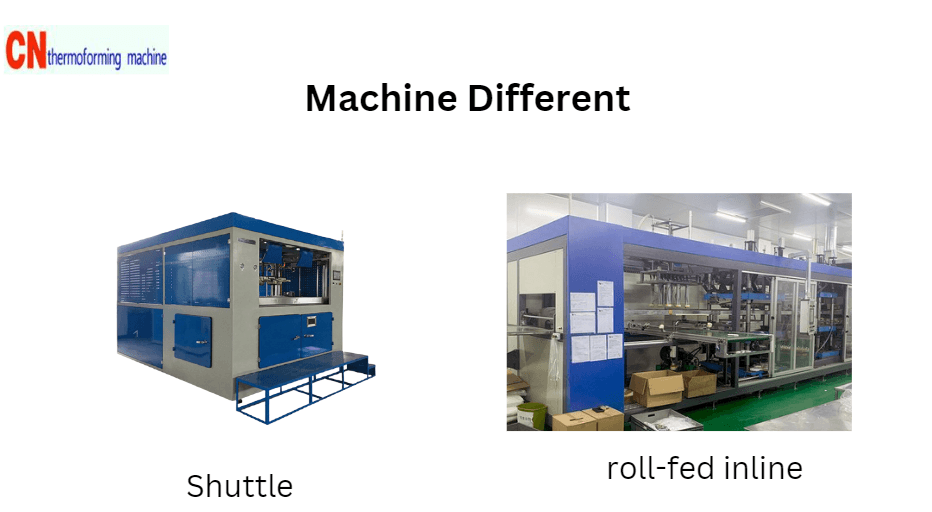
- Process Equipment: Heavy-gauge requires shuttle or rotary presses such as heavy gauge thermforming machine, while thin-gauge often uses roll-fed inline machines.
- Product Size: Heavy-gauge processes accommodate larger from large thermoforming machine factory, more robust parts with fewer mold cavities.
What is the Heavy-Gauge Thermoforming Process?
The heavy-gauge thermoforming process consists of:
- Heating: Plastic sheets are heated to their forming temperature using radiant or convection heaters.
- Forming: The heated sheet is stretched over or into a mold using vacuum or pressure. Mechanical assists like plugs may be used for complex geometries.
- Cooling: The formed part is cooled using forced air, water channels, or ambient conditions.
- Trimming and Finishing: Excess material is removed, and parts are trimmed using CNC routers or similar tools for precision.

Is Vacuum Forming or Pressure Forming Better for Heavy-Gauge Thermoforming?
- Vacuum Forming:
- Utilizes atmospheric pressure to conform the plastic to the mold.
- Best for simpler designs and lower tooling costs.
- Pressure Forming:
- Employs high air pressure to achieve finer details and better surface finishes.
- Suitable for applications requiring textured or intricate designs.
Benefits of Heavy-Gauge Thermoforming
- Cost-Effective Tooling: Lower upfront costs compared to injection molding.
- Design Flexibility: Capable of producing large, complex shapes.
- Durability: Creates strong, impact-resistant parts suitable for industrial use.
- Sustainability: Scrap material can often be recycled.
Industries Commonly Using Heavy-Gauge Thermoformed Parts
- Automotive: Dashboards, door panels, and instrument panels.
- Aerospace: Cabin walls, overhead compartments, and interior trims.
- Medical: Equipment housings and ergonomic trays.
- Industrial Equipment: Protective enclosures, panels, and bins.
What Polymers Are Used for Heavy-Gauge Thermoforming?
Common materials include:
- ABS: Offers impact strength and easy machining.
- Acrylic: Known for clarity and UV resistance.
- Polycarbonate: Strong and heat-resistant.
- HDPE: Lightweight and durable.
- TPO: Resists weather and impact.
How Long Does it Take to Thermoform a Heavy-Gauge Plastic Part?
Normally 2-4mins/cycle, however cycle times depend on:
- Material Thickness: Thicker sheets require longer heating and cooling times.
- Part Design Complexity: More intricate designs may need additional forming and trimming time.
- Cooling Requirements: Enhanced cooling techniques like water channels can accelerate cycle completion. Typically, forming a single part can take several minutes, varying by machine and material.
Heavy-gauge thermoforming remains an essential process for creating durable, high-quality parts in industries requiring reliability and precision. By understanding the materials, processes, and benefits, manufacturers can optimize their designs and applications for success.
In this Article

