How to Select the Best Material for Thermoforming: A Comprehensive Guide
Thermoforming is a widely-used manufacturing process that transforms plastic sheets into various products by heating, shaping, and cooling. Choosing the best material for thermoforming is critical to ensure product quality, functionality, and cost-effectiveness. In this article, we’ll explore the factors to consider when selecting a material, provide insights into popular options, and share actionable tips for success.
Introduction to Thermoforming Materials
Thermoforming relies on thermoplastics, which soften when heated and can be reshaped multiple times without significant degradation. These materials are versatile, cost-effective, and suitable for a wide range of applications, including packaging, automotive components, medical devices, and consumer goods.
Why Material Selection Matters
- Impacts product durability and performance.
- Influences production efficiency and cost.
- Affects environmental sustainability and recyclability.
Key Factors to Consider in Material Selection
Selecting the best material for thermoforming involves understanding several critical factors:
1. Application Requirements
- Durability: Products requiring high impact resistance may benefit from materials like ABS or HDPE.
- Aesthetics: Clear or glossy finishes may require acrylic or polycarbonate.
- Flexibility: For pliable components, consider materials like TPO or LDPE.
2. Material Properties
- Thermoforming Window: The temperature range where a material can be shaped effectively.
- Chemical Resistance: For applications exposed to harsh chemicals, HDPE and polypropylene are ideal.
- UV Resistance: Outdoor products require UV-stable materials like acrylic.
3. Cost
- Balance material quality with budget constraints. HIPS is a cost-effective option for many applications, while polycarbonate offers premium performance at a higher price.
4. Production Requirements
- Consider the forming process (vacuum, pressure, or matched die) and whether the material is compatible with your equipment.
5. Environmental Factors
- Assess the operating environment, including exposure to temperature extremes, moisture, or chemicals.
Common Thermoforming Materials and Their Properties
Below is a detailed comparison of commonly used thermoforming materials:
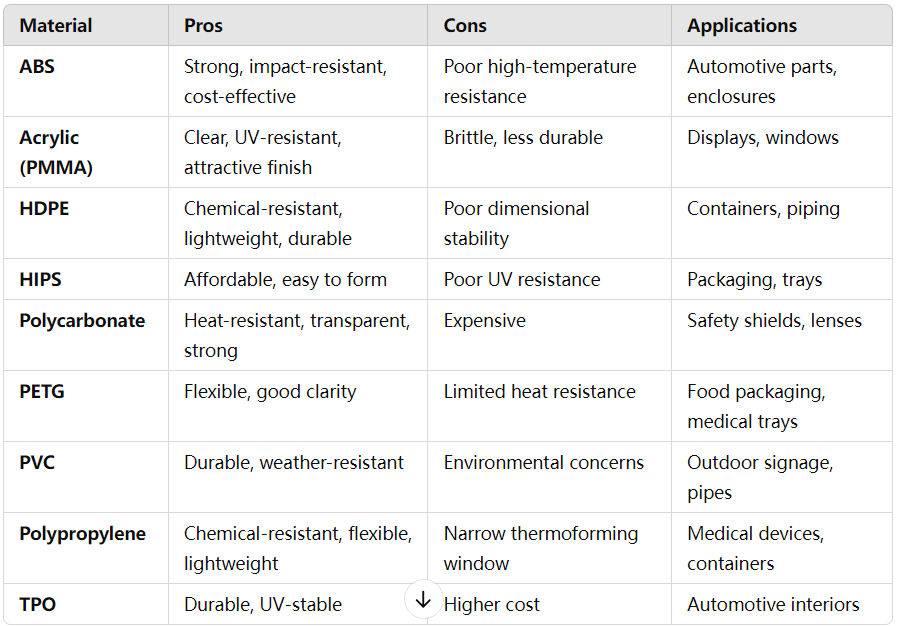
Application-Specific Material Recommendations
1. Food Packaging
- Recommended Materials: PETG, HIPS, Polypropylene
- Key Features: Food-grade, lightweight, moisture-resistant.
2. Automotive Components
- Recommended Materials: ABS, TPO, Polycarbonate
- Key Features: Durability, heat resistance, UV stability.
3. Medical Devices
- Recommended Materials: PETG, Polypropylene
- Key Features: Sterility, chemical resistance, clarity.
4. Consumer Goods
- Recommended Materials: HIPS, PVC, Acrylic
- Key Features: Aesthetic appeal, cost-effectiveness.
5. Construction and Signage
- Recommended Materials: HDPE, PVC, Polycarbonate
- Key Features: Weather resistance, durability.
Sustainability and Recycling in Thermoforming
With increasing emphasis on sustainability, selecting eco-friendly materials can enhance your product’s appeal and reduce environmental impact.
Eco-Friendly Options
- Recyclable Materials: PETG, Polypropylene, HDPE.
- Biodegradable Alternatives: Some specialty polymers are now available for environmentally-conscious applications.
Recycling Tips
- Collect and reuse production scrap.
- Choose materials that are widely accepted in recycling programs.
Tips for Testing and Prototyping Materials
- Small-Scale Prototyping: Test materials on small batches to evaluate performance.
- Use Material Data Sheets: Check properties like tensile strength, flexural modulus, and thermal resistance.
- Collaborate with Suppliers: Leverage their expertise to identify the best options.
Avoiding Common Material Selection Mistakes
- Overlooking Environmental Impact: Consider recyclability and biodegradability.
- Ignoring Application-Specific Needs: Match material properties to the end-use environment.
- Neglecting Process Compatibility: Ensure materials are compatible with forming equipment and techniques.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Selecting the best material for thermoforming requires a balance of application needs, material properties, cost, and sustainability. Whether you’re producing durable automotive components, clear packaging, or weather-resistant signage, understanding your requirements and testing materials thoroughly can lead to successful outcomes.
By considering the factors outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions, optimize production, and deliver high-quality products tailored to your industry’s needs.
FAQs
What is the most cost-effective material for thermoforming?
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is affordable and versatile, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious applications.
Which materials are best for outdoor use?
Materials like acrylic, polycarbonate, and HDPE are UV-resistant and durable for outdoor applications.
Can thermoforming materials be recycled?
Yes, many thermoplastics, such as PETG and polypropylene, are recyclable, enabling sustainable production.
