Thermoforming in Food Packaging: Benefits and Innovations
Thermoforming has revolutionized the food packaging industry with its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to create custom designs. From clamshells to vacuum-sealed trays, thermoforming provides solutions that ensure food safety, enhance shelf appeal, and reduce environmental impact. This article explores the benefits and latest innovations in thermoforming for food packaging.
1. What is Thermoforming?
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process where plastic sheets are heated until pliable, shaped using molds, and then cooled to create rigid packaging solutions. This technique is particularly popular in the food industry for producing durable, lightweight, and customizable packaging.
2. Benefits of Thermoforming in Food Packaging

Thermoforming offers a host of advantages, making it a go-to process for food packaging:
- Cost-Effectiveness: The process uses lower-cost molds compared to injection molding, reducing upfront expenses.
- Design Flexibility: Enables intricate designs, including embossed logos and functional features like compartments.
- Fast Production: High-speed production lines minimize lead times.
- Enhanced Food Safety: Provides airtight seals to maintain freshness and prevent contamination.
- Material Efficiency: Reduces waste through precise material usage and compatibility with recyclable plastics.
3. Common Thermoforming Materials for Food Packaging
Selecting the right material is critical for food packaging applications. Common materials include:
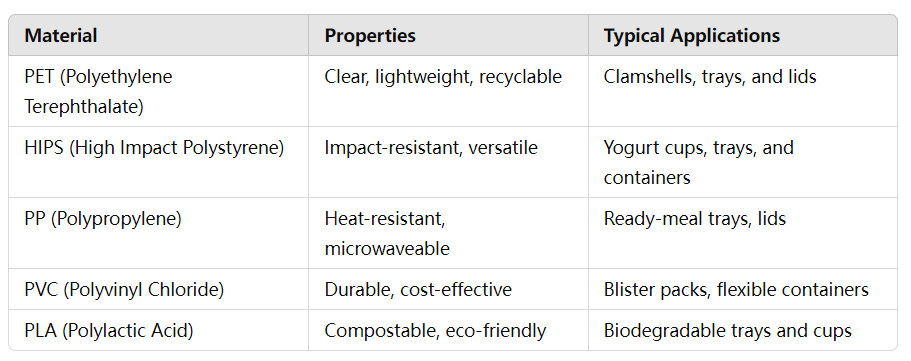
4. Innovations in Thermoforming Technology
Advanced Tooling and Precision
Modern thermoforming machines feature advanced tooling that ensures consistency and reduces material waste. Innovations in mold design allow for ultra-thin wall packaging without compromising durability.
Smart Packaging
Thermoforming integrates seamlessly with smart packaging technologies, such as QR codes and freshness indicators, enhancing consumer engagement and food safety monitoring.
High-Barrier Films
New developments in high-barrier films enhance the shelf life of perishable items by protecting against oxygen, moisture, and UV light.
5. Sustainability in Thermoformed Food Packaging
Sustainability is a growing focus in thermoforming for food packaging. Manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices, such as:
- Recyclable Materials: Transitioning to PET and rPET for better recyclability.
- Down-Gauging: Reducing material thickness to decrease plastic usage.
- Compostable Options: Using materials like PLA to meet consumer demand for biodegradable solutions.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Implementing systems to reuse post-industrial and post-consumer waste in packaging production.
6. Applications of Thermoforming in the Food Industry
Thermoforming serves a wide range of food packaging needs:
- Ready Meals: Heat-resistant trays for oven or microwave use.
- Fresh Produce: Ventilated trays and clamshells for fruits and vegetables.
- Dairy Products: Yogurt cups, butter containers, and cheese trays.
- Meat and Seafood: Vacuum-sealed trays for extended shelf life.
- Snack Packaging: Resealable containers and portioned compartments.
7. Challenges and Solutions in Thermoforming
Common Challenges
- Material Waste: Excess trim during the cutting stage.
- Uneven Heating: Can lead to inconsistent wall thickness.
- Environmental Concerns: Use of non-recyclable plastics.
Solutions
- Optimized Tool Design: Ensures uniform material distribution.
- Energy-Efficient Heaters: Reduce energy consumption and improve consistency.
- Material Innovations: Focus on biodegradable and recyclable options.
8. Future Trends in Thermoforming for Food Packaging
- Automation and AI: Improved productivity and quality control through automation.
- Digital Printing Integration: Enhances customization for brand differentiation.
- Sustainable Materials: Greater adoption of bio-based and recycled plastics.
- Smart Manufacturing: Use of IoT and real-time monitoring to optimize production.
9. Conclusion: The Thermoforming Advantage
Thermoforming continues to be a cornerstone in food packaging, offering unparalleled versatility, efficiency, and innovation. By addressing sustainability challenges and leveraging advancements in technology, the industry is poised to meet evolving consumer demands while ensuring food safety and freshness.
For businesses in the food industry, investing in thermoformed packaging not only enhances product appeal but also supports a more sustainable future.
